GOES satellites provide the kind of continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. They circle the Earth in a geosynchronous orbit, which means they orbit the equatorial plane of the Earth at a speed matching the Earth's rotation. This allows them to hover continuously over one position on the surface. The geosynchronous plane is about 35,800 km (22,300 miles) above the Earth, high enough to allow the satellites a full-disc view of the Earth.
Because GOES satellites stay above a fixed spot on the surface, they provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric 'triggers' for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms, and hurricanes. When these conditions develop the GOES satellites are able to monitor storm development and track their movements. GOES satellite imagery is also used to estimate rainfall during the thunderstorms and hurricanes for flash flood warnings, as well as estimates snowfall accumulations and overall extent of snow cover.
Such data help meteorologists issue winter storm warnings and spring snow melt advisories. Satellite sensors also detect ice fields and map the movements of sea and lake ice.
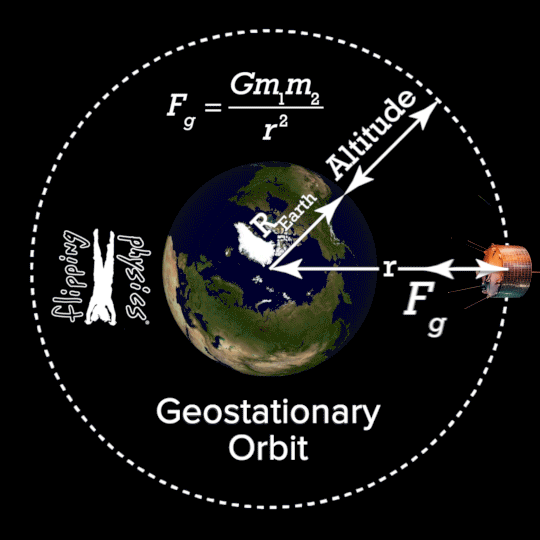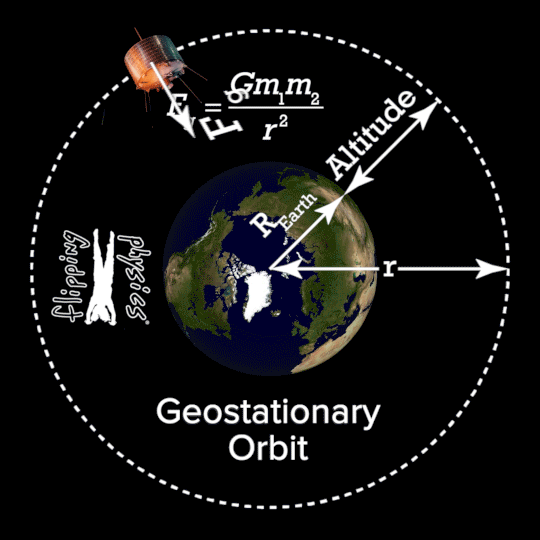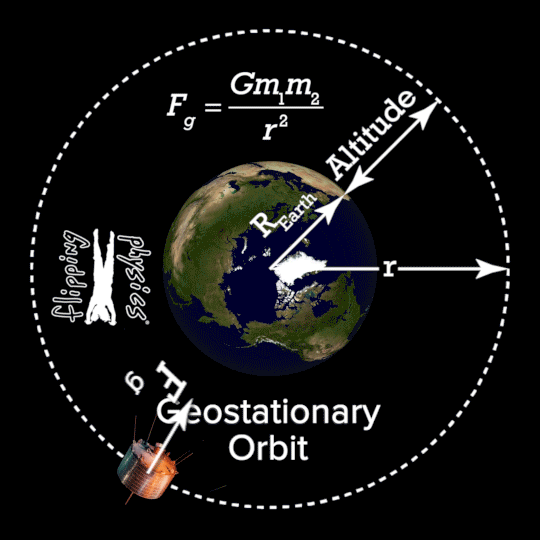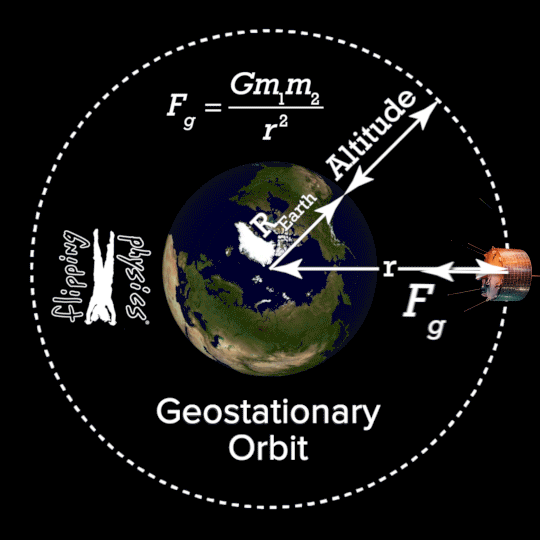
- 1.2.1 Geostationary satellites A geostationary satellite is in an orbit that can only be achieved at an altitude very close to 35,786 km (22,236 miles) and which keeps the satellite fixed over one longitude at the equator. The satellite appears motionless at a fixed position in the sky to ground observers.
- Geostationary orbit definition at Dictionary.com, a free online dictionary with pronunciation, synonyms and translation.
- The Space Science and Engineering Center (SSEC) is an internationally known research center at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. SSEC develops and utilizes instrumentation, algorithms, satellite ground and satellite archive systems to study the Earth and other planetary atmospheres.
- / dʒiː.oʊˌsteɪ.ʃ ə n. Ə r.i ˈɔːr.bɪt / an orbit (= path travelled around an object in space) in which a satellite always remains over the same place on the earth's surface because it moves at the same speed as the earth turns SMART Vocabulary: related words and phrases.
Geostationary orbit is that particular orbit where the orbital period of a satellite is equal to that of earth (24 hrs). Due to this, the position of earth and satellite is always fixed. The satellite is always present over a particular region on.
ge·o·sta·tion·ar·y
(jē′ō-stā′shə-nĕr′ē)adj.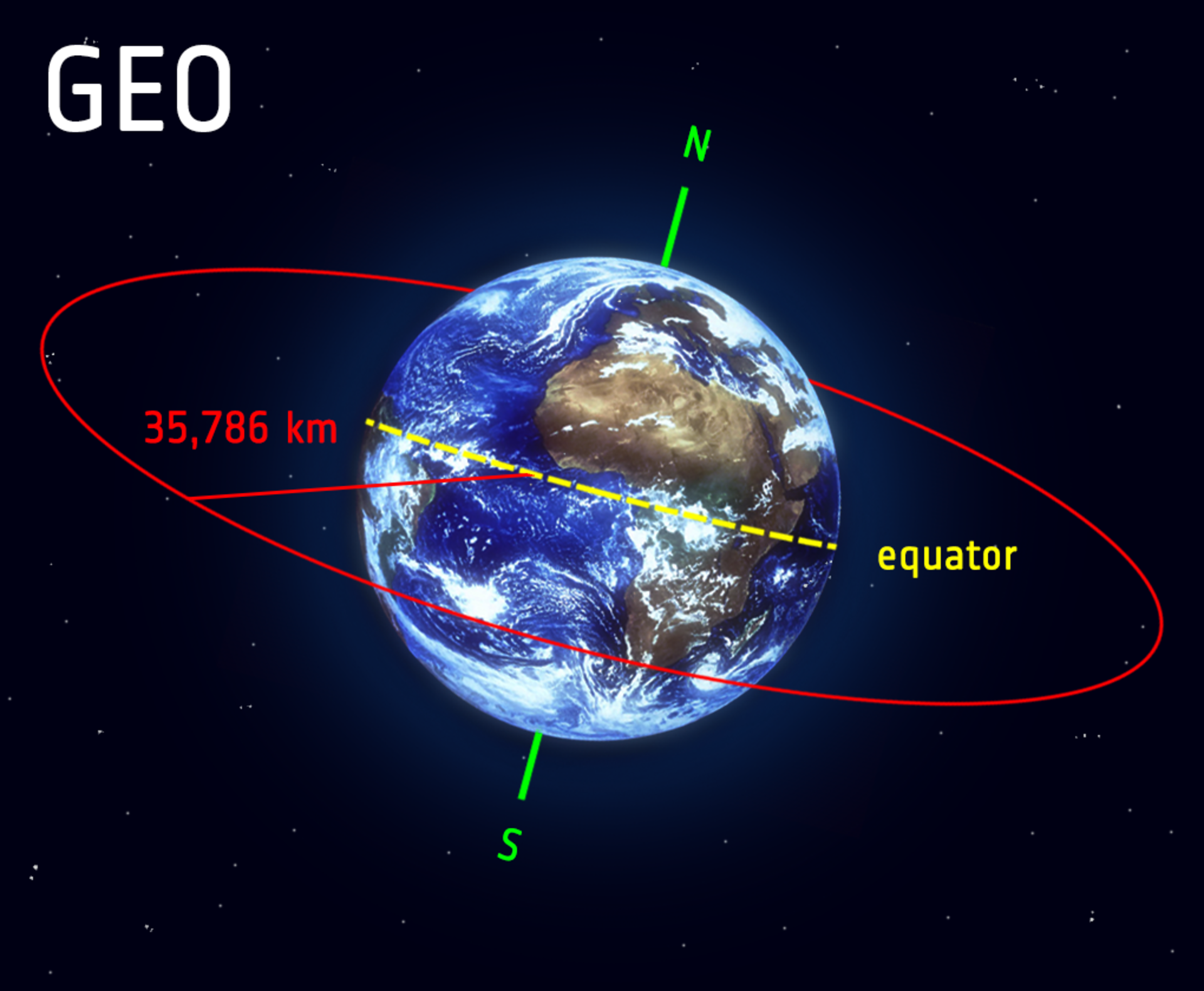
geostationary
(Geostationary Orbit
ˌdʒiːəʊˈsteɪʃənərɪ) adjge•o•sta•tion•ar•y
(ˌdʒi oʊˈsteɪ ʃəˌnɛr i)adj.
| Adj. | 1. | geostationary - of or having a geosynchronous orbit such that the position in such an orbit is fixed with respect to the earth; 'a geostationary satellite' fixed - securely placed or fastened or set; 'a fixed piece of wood'; 'a fixed resistor' |
geostationary
[ˌdʒiːəʊˈsteɪʃənərɪ]ADJ → geoestacionariogeostationary

Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content.
Geostationary Orbit Definition
Link to this page:Geostationary Definition
